In this article, we will discuss some important and frequently asked Java 8 Stream API Interview Questions and Answers.
Introduced in Java 8, the Stream API is used to process collections of objects. A stream is a sequence of objects that supports various methods which can be pipelined to produce the desired result.

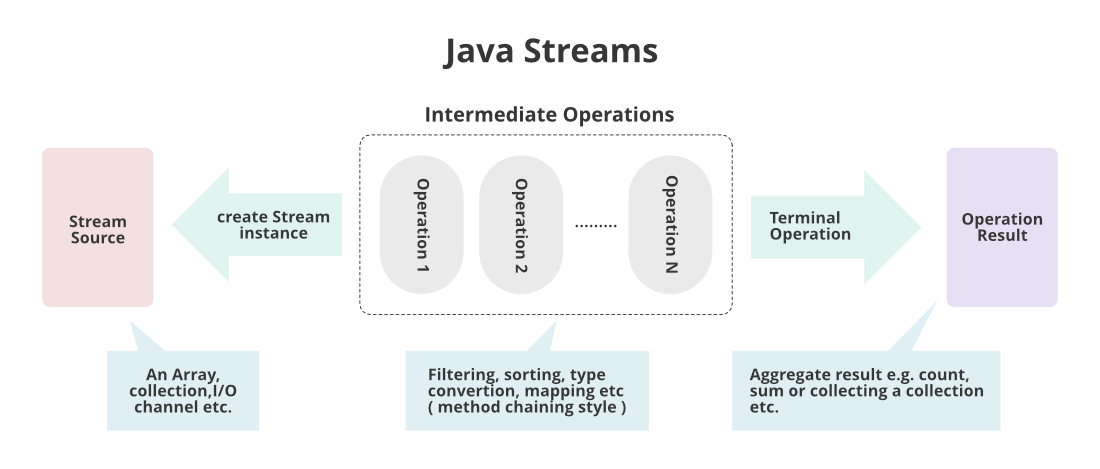
Stream does not store elements. It simply conveys elements from a source such as a data structure, an array, or an I/O channel, through a pipeline of computational operations.
Stream is functional in nature. Operations performed on a stream do not modify its source. For example, filtering a Stream obtained from a collection produces a new Stream without the filtered elements, rather than removing elements from the source collection.
Intermediate operations transform a stream into another stream, such as filtering, sorting, element transformation (mapping)
Java Stream Example: Filtering using Stream.filter() method:List Product > productsList = new ArrayList < Product > (); // Adding Products productsList.add(new Product(1, "HP Laptop", 25000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(2, "Dell Laptop", 30000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(3, "Lenevo Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(4, "Sony Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(5, "Apple Laptop", 90000 f)); // This is more compact approach for filtering data productsList.stream().filter(product -> product.getPrice() == 30000) .forEach(product -> System.out.println(product.getPrice()));
30000.0List Product > productsList = new ArrayList < Product > (); // Adding Products productsList.add(new Product(1, "HP Laptop", 25000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(2, "Dell Laptop", 30000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(3, "Lenevo Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(4, "Sony Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(5, "Apple Laptop", 90000 f)); // Converting product List into Set Set Float > productPriceList = productsList.stream().filter(product -> product.getPrice() 30000) .map(product -> product.getPrice()).collect(Collectors.toSet()); System.out.println(productPriceList);
A terminal operation that produces a result, such as a forEach, min, max, count, sum, or a new collection.
Example 1: The Java Stream forEach() the method is a terminal operation: List stringList = new ArrayList<>(); stringList.add("one"); stringList.add("two"); stringList.add("three"); stringList.add("one"); Stream stream = stringList.stream(); stream.forEach( element -> < System.out.println(element); >);
one two three oneList Product > productsList = new ArrayList < Product > (); // Adding Products productsList.add(new Product(1, "HP Laptop", 25000f)); productsList.add(new Product(2, "Dell Laptop", 30000f)); productsList.add(new Product(3, "Lenevo Laptop", 28000f)); productsList.add(new Product(4, "Sony Laptop", 28000f)); productsList.add(new Product(5, "Apple Laptop", 90000f)); // max() method to get max Product price Product productA = productsList.stream() .max((product1, product2) -> product1.getPrice() > product2.getPrice() ? 1 : -1).get(); System.out.println(productA.getPrice()); // min() method to get min Product price Product productB = productsList.stream() .max((product1, product2) -> product1.getPrice() product2.getPrice() ? 1 : -1).get(); System.out.println(productB.getPrice());
Here are the examples to create a Stream using different sources such as Array, Collections, String, etc.
StreamString> stream = Stream.empty(); stream.forEach(System.out::println);
CollectionString> collection = Arrays.asList("JAVA", "J2EE", "Spring", "Hibernate"); StreamString> stream2 = collection.stream(); stream2.forEach(System.out::println); ListString> list = Arrays.asList("JAVA", "J2EE", "Spring", "Hibernate"); StreamString> stream3 = list.stream(); stream3.forEach(System.out::println); SetString> set = new HashSet<>(list); StreamString> stream4 = set.stream(); stream4.forEach(System.out::println);
An Array can be a source of a Stream or an Array can be created from the existing array or of a part of an array:
// Array can also be a source of a Stream StreamString> streamOfArray = Stream.of("a", "b", "c"); streamOfArray.forEach(System.out::println);
We can also use String as a source for creating a stream with the help of the chars() method of the String class.
IntStream streamOfChars = "abc".chars();Read more about streams at Java 8 Stream APIs with Examples.
1. Collections are used to store and group the data in a particular data structure like List, Set, or Map. Whereas Streams are used to perform complex data processing operations like filtering, matching, mapping, etc on stored data such as arrays, collections, or I/O resources. That means, collections are mainly about data and streams are mainly about operations on data.
Example 1: List collection is used to store data// Creating an ArrayList of String using ListString> fruits = new ArrayList<>(); // Adding new elements to the ArrayList fruits.add("Banana"); fruits.add("Apple"); fruits.add("mango"); fruits.add("orange");Example 2: Streams are used to perform operations like filtering, mapping, collection result, etc:
List lines = Arrays.asList("java", "c", "python"); List result = lines.stream() // convert list to stream .filter(line -> !"c".equals(line)) // we dont like c .collect(Collectors.toList()); // collect the output and convert streams to a List result.forEach(System.out::println); 2. You can add to or remove elements from collections. But, you can’t add to or remove elements from streams. Stream consumes a source, performs operations on it, and returns a result. They don’t modify even the source also.
For example:// Creating an ArrayList of String using List String > fruits = new ArrayList < >(); // Adding new elements to the ArrayList fruits.add("Banana"); fruits.add("Apple"); fruits.add("Mango"); fruits.add("Orange"); fruits.add("Pineapple"); fruits.add("Grapes"); System.out.println(fruits); // Remove the element at index `5` fruits.remove(5); System.out.println("After remove(5): " + fruits);In Streams, there are no such methods to add or remove elements.
3. The main specialty of Java 8 Streams is that you need not worry about iteration while using Streams. Streams perform iteration internally behind the scene for you (using the forEach() method). You just have to mention the operations to be performed on a source.
On the other hand, you have to do the iteration externally over collections using loops.
Example 1: External iterations of Collections using for loops// Creating an ArrayList of String using ListString> fruits = new ArrayList<>(); // Adding new elements to the ArrayList fruits.add("Banana"); fruits.add("Apple"); fruits.add("mango"); fruits.add("orange"); fruits.add("Watermelon"); fruits.add("Strawberry"); System.out.println("\n=== Iterate using for loop with index ==="); for(int i = 0; i fruits.size(); i++) < System.out.println(fruits.get(i)); > System.out.println("=== Iterate using Java 8 forEach and lambda ==="); fruits.forEach(fruit -> < System.out.println(fruit); >);Example 2: Internal iteration of Streams. No more for loops:
List lines = Arrays.asList("java", "c", "python"); List result = lines.stream() // convert list to stream .filter(line -> !"c".equals(line)) // we dont like c .collect(Collectors.toList()); // collect the output and convert streams to a List result.forEach(System.out::println); 4. Streams are traversable only once. If you traverse the stream once, it is said to be consumed. To traverse it again, you have to get a new stream from the source again. But, collections can be traversed multiple times.
ListInteger> numbers = Arrays.asList(4, 2, 8, 9, 5, 6, 7); StreamInteger> numbersGreaterThan5 = numbers.stream().filter(i -> i > 5); //Traversing numbersGreaterThan5 stream first time numbersGreaterThan5.forEach(System.out::println); //Second time traversal will throw error //Error : stream has already been operated upon or closed numbersGreaterThan5.forEach(System.out::println);
The map() function is an intermediate function that is used to perform map functional operations in Java. This means it can transform one type of object to others by applying a function.
Use map() function to convert one object to another object.
For example, if you have a List of String and you want to convert that to a List of Integer, you can use map() to do so.
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < ListlistOfStrings = Arrays.asList("1", "2", "3", "4", "5"); List listOfIntegers = listOfStrings.stream() .map(Integer::valueOf) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(listOfIntegers); > > [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]Java stream provides a filter() method to filter stream elements on the basis of a given predicate. This method takes a predicate as an argument and returns a stream consisting of resulted elements.
Example 1: Using filter() method to filter List of string objects:
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; public class Tester < public static void main(String[] args)< Listlines = Arrays.asList("java", "c", "python"); List result = lines.stream() // convert list to stream .filter(line -> !"c".equals(line)) // we dont like c .collect(Collectors.toList()); // collect the output and convert streams to a List result.forEach(System.out::println); > > java pythonExample 2: In this example, we will create a list of products and we filter products whose price is greater than 25k. We display a list of products using the forEach() method.
Let's first create a Product class:class Product < private int id; private String name; private float price; // getters and setters >
public class StreamFilterExample < public static void main(String[] args) < // using stream API List Product > filteredProducts = getProducts().stream() .filter((product) -> product.getPrice() > 25000 f) .collect(Collectors.toList()); filteredProducts.forEach(System.out::println); > private static List < Product > getProducts() < List Product > productsList = new ArrayList < Product > (); productsList.add(new Product(1, "HP Laptop", 25000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(2, "Dell Laptop", 30000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(3, "Lenevo Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(4, "Sony Laptop", 28000 f)); productsList.add(new Product(5, "Apple Laptop", 90000 f)); return productsList; > >
In the above example, we are using the filter() method to filter products whose price is greater than 25k:
List Product > filteredProducts = getProducts().stream() .filter((product) -> product.getPrice() > 25000 f) .collect(Collectors.toList());
The Stream.flatMap() function, as the name suggests, is the combination of a map and a flat operation. This means you first apply the map function and then flatten the result.
To understand what flattening a stream consists in, consider a structure like [ [1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9] ] which has "two levels". It's basically a big List containing three more List. Flattening this means transforming it in a "one level" structure e.g. [ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 ] i.e. just one list.
For example: In the below program, you can see that we have three lists that are merged into one by using a flatMap() function.
import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; import java.util.stream.Collectors; import java.util.stream.Stream; public class Main < public static void main(String[] args) < Listevens = Arrays.asList(2, 4, 6); List odds = Arrays.asList(3, 5, 7); List primes = Arrays.asList(2, 3, 5, 7, 11); List numbers = Stream.of(evens, odds, primes) .flatMap(list -> list.stream()) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("flattend list: " + numbers); > > flattend list: [2, 4, 6, 3, 5, 7, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11]The intermediate Stream operation returns another Stream, which means you can further call other methods of Stream class to compose a pipeline.
Intermediate Stream operations:// Converting product List into Set Set Float > productPriceList = productsList.stream().filter(product -> product.getPrice() 30000) .map(product -> product.getPrice()).collect(Collectors.toSet());Stream terminal operation produces a result other than Streams like a value or a Collection. Terminal Stream operations:
Once a terminal method like forEach() or collect() is called, you cannot call any other method of Stream or reuse the Stream.”
List lines = Arrays.asList("java", "c", "python"); List result = lines.stream() // convert list to stream .filter(line -> !"c".equals(line)) // we dont like c .collect(Collectors.toList()); // collect the output and convert streams to a List result.forEach(System.out::println);